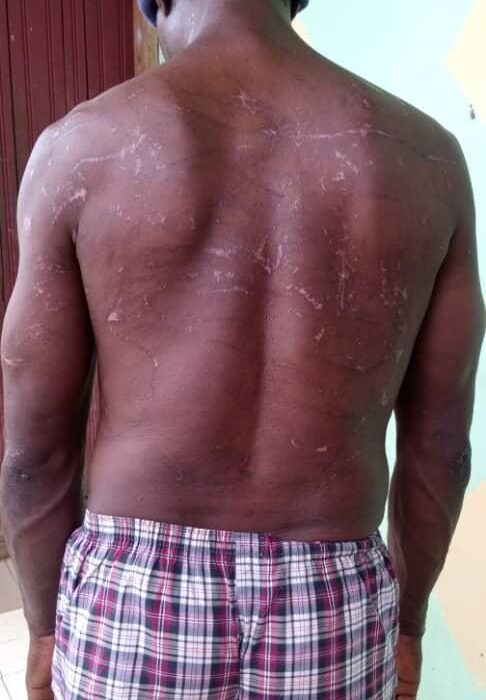
Justice for Mandong Henry Disturbing, degrading and inhumane treatment of the innocent.
The Anglophone crisis which has been ongoing for the past seven years has now spiralled into an unimaginable death-trap for the people of Southern Cameroons. Despite the skyrocketing violence, the ruling government is not showing any willingness to either come to the negotiation table nor initiate other approaches to bring an end to the bloody conflict. On the contrary, victimizing civilians has become a war strategy for the regime in their attempt to force the people to give up on their rights to self determination. On countless occasions, government forces have been guilty of war crimes, indiscriminate shooting of civilians, arbitrarily arrests, inhumane detention and torture.
With no end of the war in sight, what fate for the people of Southern Cameroons who after being subjected to over 50years of profound historical alienation, marginalization, and discrimination are now being subjugated to the gruesome experience of genocide; one of the worst of our times.
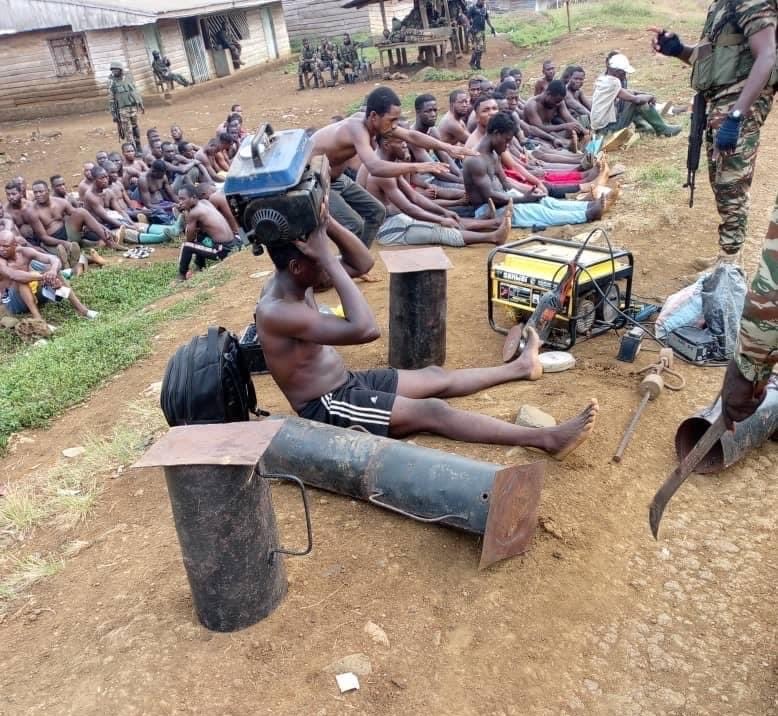
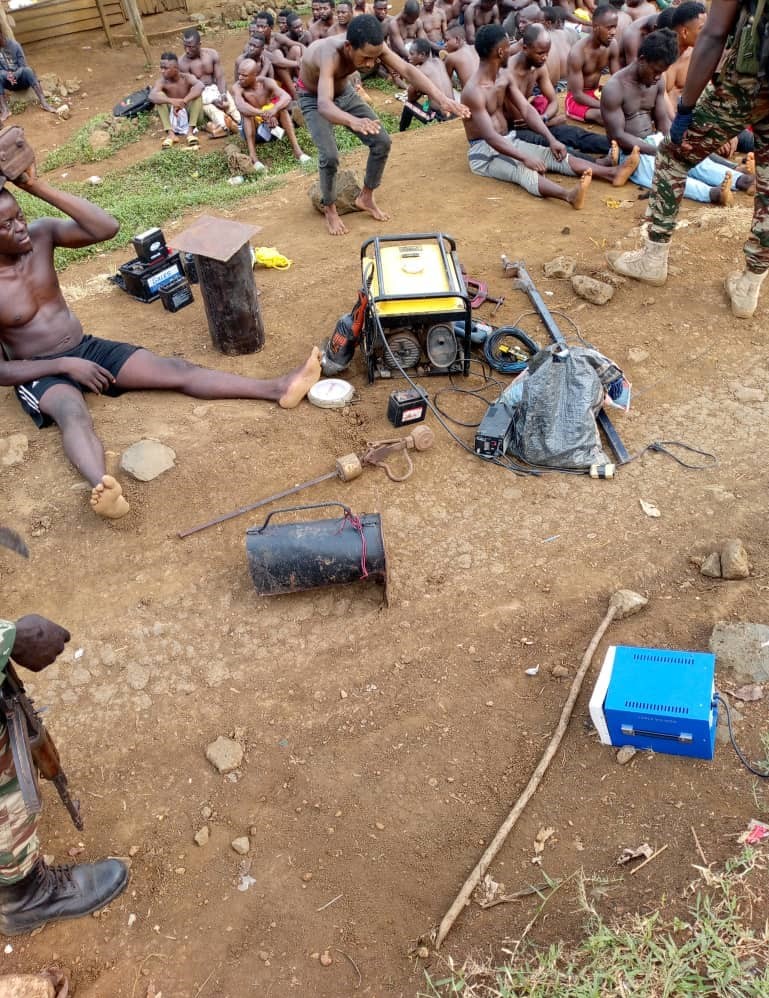
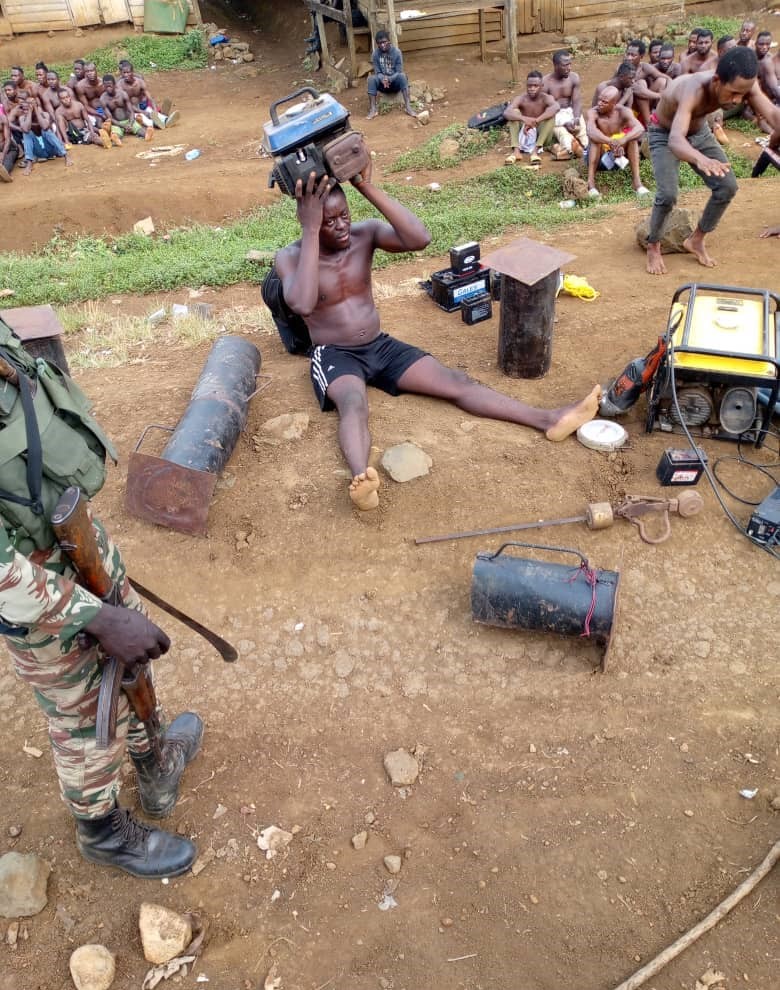
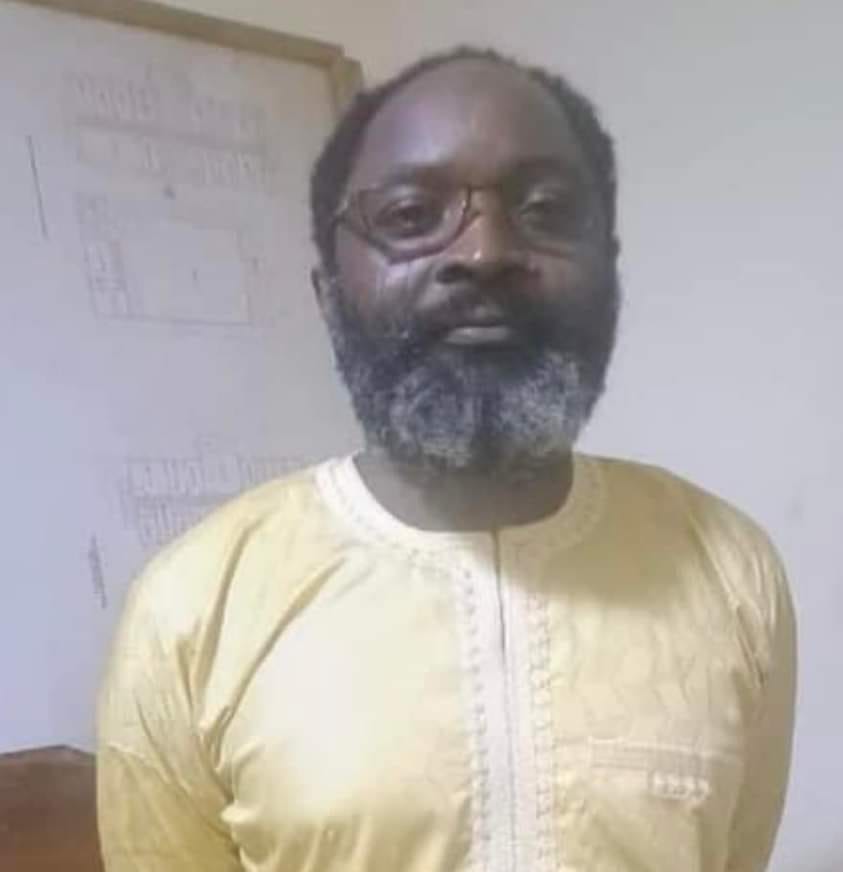
At this point, the ordeal of Mandong Henry, a Southern Cameroonian who lives in Yaounde comes to mind. His predicament began on June the 6th, 2023, when he was arbitrarily arrested by elements of the national gendarme forces from his residence at Biyem-Assi neighbourhood. In narrating the incident, Human Rights Lawyer Barrister Tamfu Richard stated that he was taken to the gendarme headquarters in Yaounde, handcuffed. On arrival, they stripped him off his clothes and tied him to a mango tree with the handcuffs on for two days. He spent the entire two days tied onto the tree with no food nor water. As if that was not enough, he was then tortured by gendarmes. Turn by turn, they brutally beat him on the back mercilessly with machetes, sticks, iron rods, and electric cables. Although the torturing left his back completely covered with wounds, he was not taken to the hospital; but instead thrown into detention at SED (State Defence Secretariat). in the cause of torturing him, his left eye was almost damaged.
Mandong Henry was allegedly accused of being involved in a plot to transport an explosive in a bag from Bamenda to Yaounde. At the time of his accusation, he worked as a loader for an inter-urban bus agency that transported passengers from Bamenda to Yaounde. No investigation was carried out before his arrest. Neither was he convicted of the alleged accusations. Again, another southern Cameroonian had to innocently suffer from unlawful arrest, torture and detention.
Since the beginning of the anglophone crisis, the rate at which the human rights of Southern Cameroonians are being violated by the forces of the Cameroonian government is particularly concerning. I can say it portrays a deeply rooted deadly hatred and that is why the cause of the Anglophone Crisis needs to be addressed from it’s roots. That hatred can be felt and seen from the atrocities that are being committed against the people of Southern Cameroons because of the ongoing conflict.
We, as a people and a nation deserve the right to a safe and secure future. War crimes are surging at an exponential rate, as the regime continues to deploy military forces on a daily basis to the North West and South west Regions Of Southern Cameroons. Instead of protecting the population, they kill, abduct, force disappearances, raid and set villages ablaze.
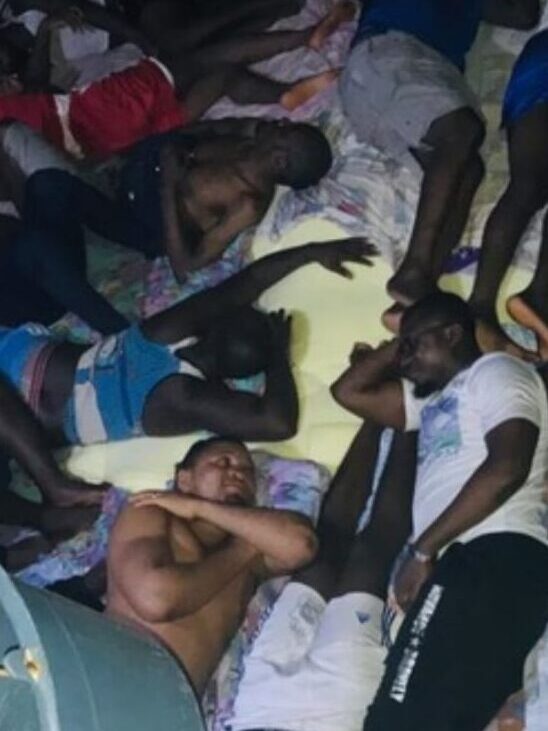
Thousands have been displaced for lack of food, shelter and adequate medical care. Several thousands are suffering in the bushes. Reportedly, soldiers are killing civilians fleeing and searching for safety. On the 17th of June 2023, 12 civilians were killed while they were fleeing from military raid at Big Babanki, in the North West Region of Southern Cameroons.
The Big Babanki Massacre.

This again attests to the fact that there is no safe place for Southern Cameroonians in Cameroon. This conflict has caused untold hardship and sufferings to our people and according to a United Nations report, over 4.7million people are in dying need of humanitarian assistance.
Human rights are the cornerstone of the United Nations and we call for the international Community to initiate peace talks and compel Cameroon to come to the negotiation table. This is to raise the awareness that there is an ongoing genocide in Southern Cameroons, and to urge the initiation of peace talks to end the conflict.
#endanglophonecrisis
Justice for Mandong Henry
Our human rights matter.
Author: Dorothy Arrey
Freedom fighter and Humanitarian Lead
Follow on twitter for more at Dorothy Arrey